Boost Healthcare: CRM System for Doctors & Hospitals | Patients
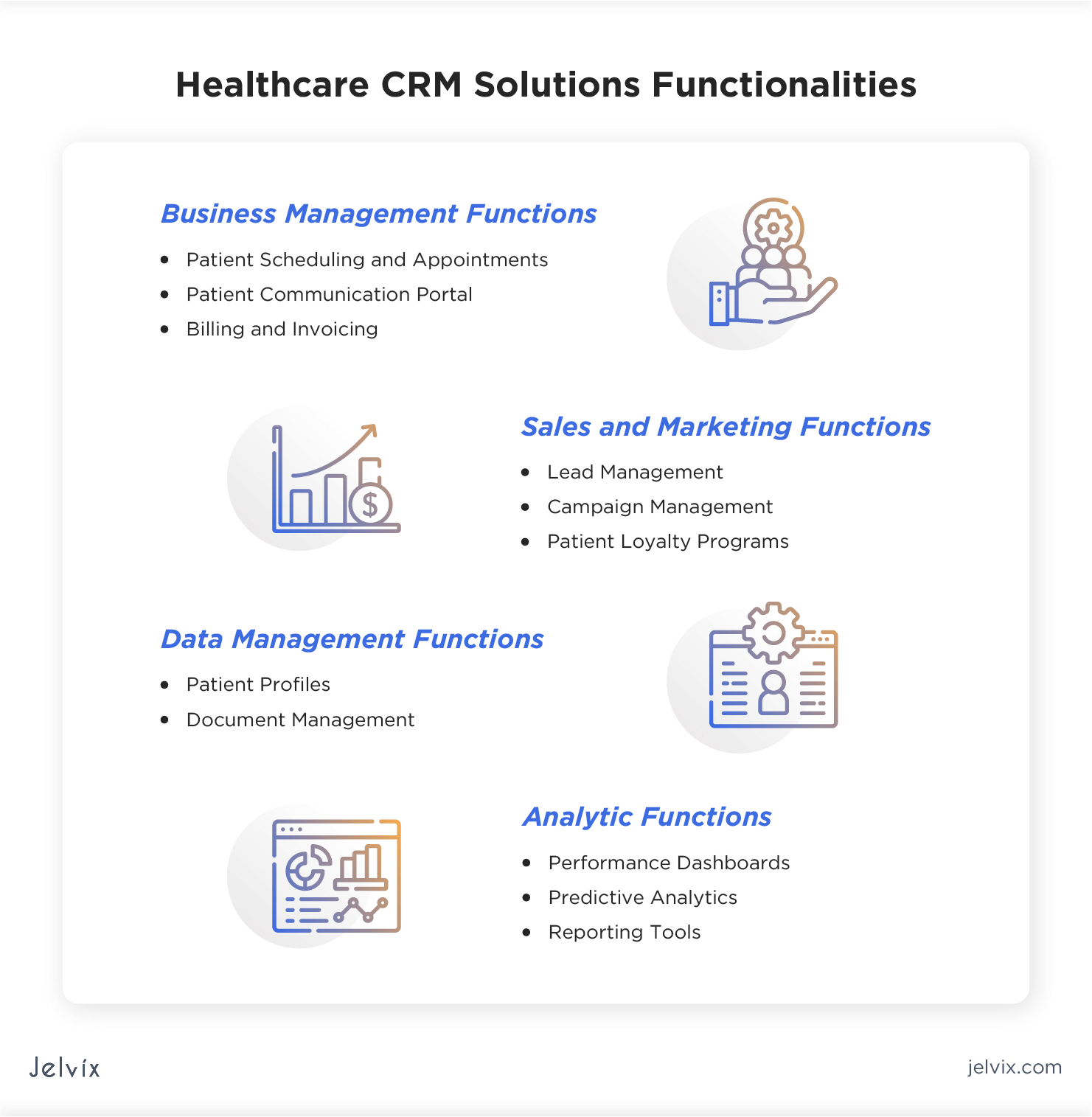
Zonamotoblog.blogspot.com - Boost healthcare with CRM systems for doctors and hospitals. Enhance patient management, streamline workflows, and improve care delivery. A Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system, specifically tailored for medical professionals and healthcare institutions, represents a sophisticated digital platform engineered to manage and analyze patient interactions and data throughout the patient lifecycle. This specialized platform consolidates information from various touchpoints, including appointments, medical history, communication logs, and billing, into a centralized database. For instance, such a solution enables a clinic to track patient outreach for preventative screenings, manage follow-up appointments efficiently, or record feedback from patient satisfaction surveys, thereby creating a comprehensive view of each individual's engagement with the healthcare provider.
The implementation of these healthcare-specific systems is paramount in today's intricate medical landscape. Benefits include enhanced patient engagement through personalized communication, improved operational efficiency by automating administrative tasks, and better decision-making capabilities derived from robust data analytics. Historically, patient data was often fragmented across paper charts and disparate departmental databases. The evolution towards integrated digital infrastructure marks a significant advancement, fostering a more cohesive and responsive approach to patient care and institutional management.
Further exploration of this technology typically delves into its specific features, such as appointment scheduling modules, electronic health record (EHR) integration, secure messaging capabilities, and referral management tools. Understanding the implementation process, potential challenges, and key considerations for selecting the most appropriate platform for a given medical practice or hospital network forms the subsequent critical layers of insight into this indispensable aspect of modern healthcare operations.
The Indispensable Role of CRM Systems for Doctors and Hospitals
The comprehensive examination of a CRM system for doctors and hospitals has illuminated its foundational significance within contemporary healthcare. This specialized digital infrastructure serves as a pivotal tool for centralizing patient interaction data, streamlining administrative processes, and fostering robust patient relationships. It has been established that such a system, while distinct from clinical EHR/EMR platforms, critically complements them by focusing on the patient journey, communication efficacy, and overall service delivery. Key aspects underscored throughout this discussion include the imperative for stringent data security and regulatory compliance, the necessity of seamless integration with existing healthcare technologies, and the absolute requirement for comprehensive staff training to ensure successful adoption and optimal utilization.
The strategic deployment and continuous optimization of a CRM system for doctors and hospitals are no longer mere advantages but have become fundamental prerequisites for institutions committed to delivering exceptional patient care and achieving operational excellence. In an increasingly competitive and patient-centric environment, the capacity to harness data for personalized engagement, efficient resource management, and informed decision-making is paramount. Healthcare organizations must recognize this technology not simply as an investment, but as a core enabler for future sustainability, enhanced patient loyalty, and the advancement of public health outcomes. Proactive embrace and continuous refinement of these systems will undoubtedly define the trajectory of modern healthcare delivery.
Strategic Implementation Guidelines for Healthcare Patient Relationship Management Systems
The successful deployment and ongoing optimization of specialized patient relationship management systems are critical for maximizing their value within healthcare organizations. Adherence to best practices ensures improved patient outcomes, enhanced operational efficiency, and a robust return on investment. The following guidelines provide actionable insights for effective utilization.
Tip 1: Define Clear, Measurable Objectives Prior to Implementation. Before system acquisition or deployment, it is imperative to establish specific, quantifiable goals. These objectives should align with the organization's strategic healthcare delivery aims. For instance, a clear objective might be to reduce patient no-show rates by 15% within the first year through automated reminders, or to increase patient satisfaction scores regarding communication by 10% within six months.
Tip 2: Prioritize Robust Data Security and Regulatory Compliance. Given the sensitive nature of protected health information (PHI), stringent security protocols are non-negotiable. The chosen system must demonstrate capabilities for advanced encryption, comprehensive access controls, regular security audits, and strict adherence to relevant data privacy regulations, such as HIPAA, GDPR, or other regional standards. This ensures the integrity and confidentiality of patient data throughout its lifecycle.
Tip 3: Ensure Seamless Integration with Existing Clinical and Administrative Systems. A standalone patient relationship management system offers limited utility. Optimal performance is achieved through deep integration with Electronic Health Records (EHRs), Electronic Medical Records (EMRs), billing systems, and appointment scheduling platforms. This facilitates a unified view of the patient, eliminates data silos, reduces manual data entry, and improves data accuracy across the healthcare ecosystem.
Tip 4: Invest Substantially in Comprehensive Staff Training and Ongoing Support. User adoption is a primary determinant of system success. All staff members, from front-desk personnel to clinical practitioners and administrative leaders, must receive thorough training tailored to their specific roles and interactions with the system. Continuous education, accessible support resources, and regular refresher courses are essential to maintain proficiency and adapt to system updates.
Tip 5: Customize System Workflows to Mirror Unique Practice and Hospital Needs. Generic patient relationship management functionalities often require adaptation to align with specific clinical specialties, organizational structures, and patient care pathways. Customization may involve configuring unique patient communication templates, designing specific intake forms, or tailoring reporting dashboards to provide relevant performance metrics for various departments.
Tip 6: Leverage Advanced Analytics for Proactive Decision-Making. These systems are powerful tools for data collection; their true value lies in the actionable insights derived from that data. Utilizing integrated analytics capabilities allows for the identification of patient trends, optimization of outreach campaigns, assessment of service effectiveness, and anticipation of patient needs, thereby enabling more informed and proactive management decisions.
Tip 7: Establish a Framework for Continuous System Evaluation and Optimization. Technology and patient expectations evolve, necessitating ongoing review of the system's performance and utility. Regular assessment of key performance indicators (KPIs), solicitation of user feedback, and exploration of new features or modules ensure the system remains aligned with organizational goals and continues to deliver maximum value over time.
Adherence to these strategic guidelines facilitates the transformation of a technological investment into a core asset for patient engagement, operational excellence, and data-driven healthcare delivery. A well-implemented and managed patient relationship management system fundamentally enhances the patient journey and strengthens the relationship between healthcare providers and the communities they serve.
The preceding discussion on best practices underscores the multifaceted approach required for successful system deployment. Further consideration will now be given to the overarching implications for modern healthcare leadership and strategic planning.
Frequently Asked Questions Regarding Patient Relationship Management in Healthcare
A comprehensive understanding of patient relationship management solutions within the healthcare sector is crucial for effective adoption and utilization. The following addresses common inquiries regarding these specialized systems.
Question 1: What is the fundamental purpose of a patient relationship management system in a healthcare setting?
The primary objective is to centralize and optimize all interactions between patients and healthcare providers. This involves tracking communication, managing appointments, understanding patient preferences, and improving the overall patient journey from initial contact through ongoing care.
Question 2: How does such a system differ from Electronic Health Records (EHR) or Electronic Medical Records (EMR) systems?
While both manage patient data, EHR/EMR systems primarily focus on the clinical aspects of patient care, documenting medical history, diagnoses, treatments, and prescriptions. Patient relationship management systems, conversely, concentrate on the administrative, communicative, and relational aspects, aiming to enhance the patient experience, streamline non-clinical workflows, and support marketing or outreach initiatives. Integration between these systems is common and highly beneficial.
Question 3: What are the primary benefits for patient care and operational efficiency derived from its implementation?
Significant benefits include enhanced patient satisfaction through personalized communication and proactive engagement, reduced administrative burden via automated processes for scheduling and reminders, and improved resource allocation. Furthermore, data analytics capabilities allow for better identification of patient needs and the optimization of service delivery.
Question 4: What security considerations are paramount for these systems due to the sensitive nature of patient data?
Data security and patient privacy are critical. Systems must adhere to strict regulatory compliance standards, such as HIPAA in the United States or GDPR in Europe. This necessitates robust encryption, access controls, regular security audits, and comprehensive data backup and recovery protocols to protect sensitive health information from unauthorized access or breaches.
Question 5: What challenges are typically encountered during the implementation of these specialized systems?
Common challenges include data migration from legacy systems, ensuring seamless integration with existing clinical and billing platforms, user adoption resistance among staff, and the initial investment cost. Comprehensive planning, thorough staff training, and strong leadership support are essential for overcoming these hurdles.
Question 6: How does such a system facilitate patient engagement and retention?
Engagement is fostered through targeted communications, such as health education materials or preventative care reminders. Personalized interactions, efficient appointment management, and streamlined feedback mechanisms contribute to a positive patient experience, which in turn enhances patient loyalty and retention. The system provides the tools to proactively manage these relationships.
These systems are indispensable for modern healthcare organizations aiming to elevate patient experience, streamline operations, and ensure data integrity and security. Their strategic deployment offers a significant competitive advantage and contributes to higher standards of patient care.
The preceding discussion clarified common aspects; further exploration will delve into specific feature sets and the strategic implications for healthcare leadership.
